What is friction stir welding?
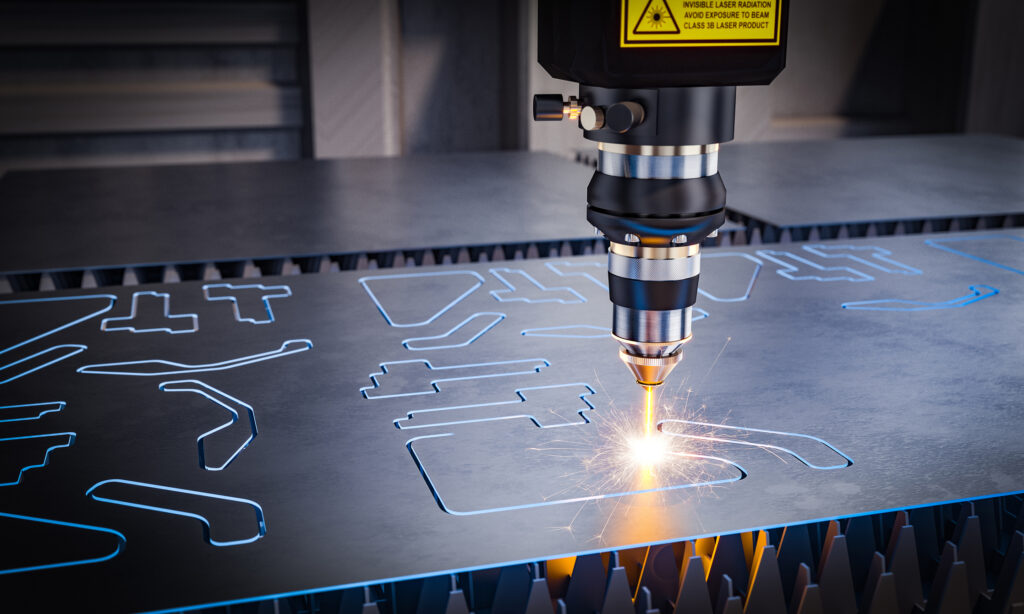
Friction stir welding, also known as FSW for Friction Stir Welding was developed in Great Britain in 1991 and patented by Wayne Thomas. This process is similar to rotary friction welding. It is used for welding sheet metal.
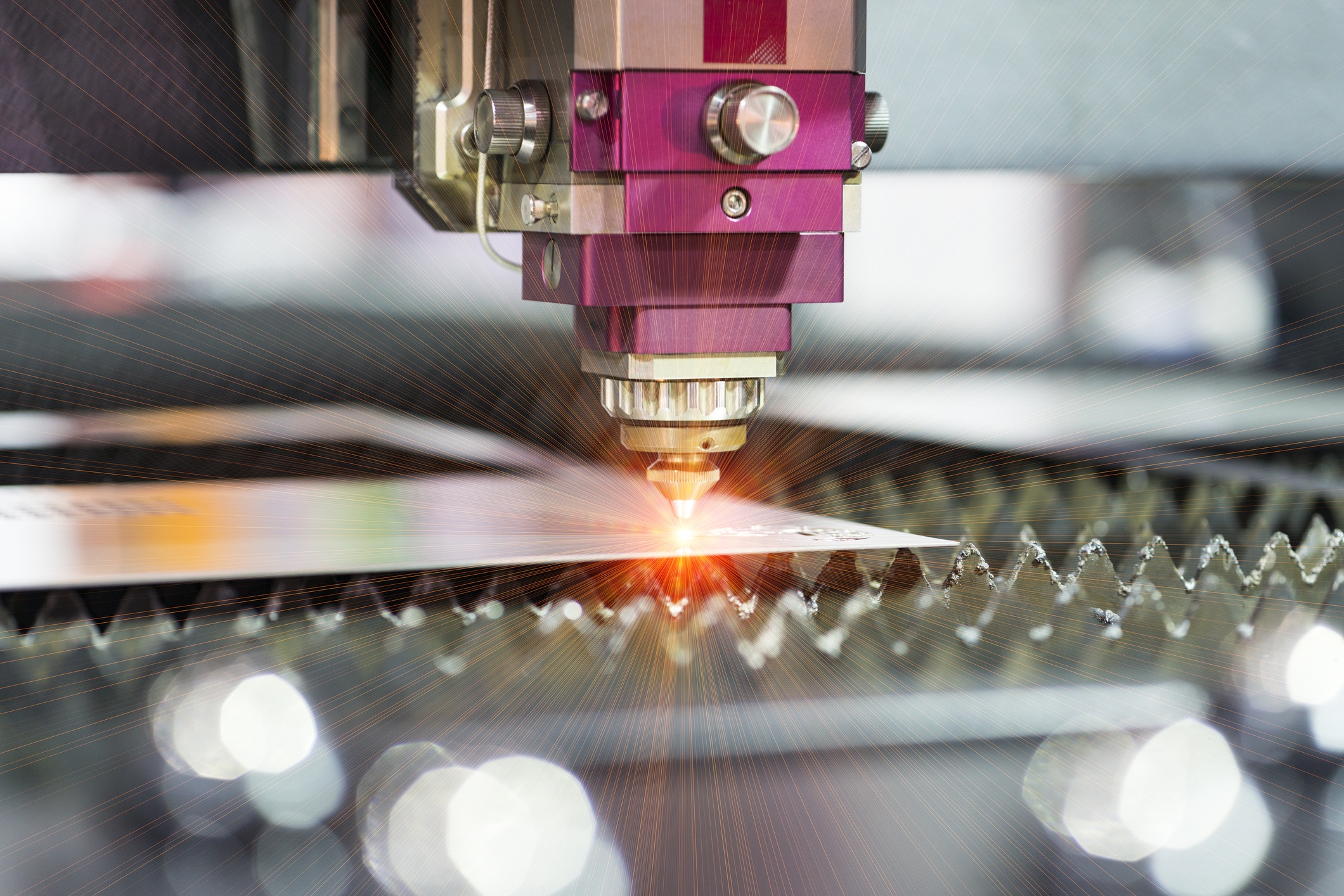
These are now joined using a rotating mould. This plasticises the material. This means that it is not yet hot enough to melt, but also no longer cold enough to be solid. The rotating tool, a pin, comes with a thread that mixes the plasticised material of both materials and thus connects them. The result is an extrusion channel that extends to the root of the seam and is often referred to as a weld nugget.
Only the pin moves, while the workpieces themselves remain stationary. There is a shoulder on the tool perpendicular to the pin, the diameter of which exceeds that of the pin. This serves to keep the outside air away from the weld seam. The tool itself pierces the surface of the workpieces at an angle of 2° or 3°.
For this welder processes no additive is required. There is also no structural change, while at the same time the seam achieves very high strength. There is also no welding fume and the heat-affected zone reaches temperatures of 550 °C or less. This means that the microstructure is not negatively affected and it is also not possible for pores to form within the material.
How does the friction stir welding process work?
At the beginning of the process, this had the disadvantage of cratering. This occurred at the end of the weld seam due to the shape of the tool used. However, newer methods prevent this by using a pin that retracts automatically.
A special extra is that defects in castings can also be levelled out using this process. If the casting has a poor surface with pores, these can be transformed into a smooth and excellent surface using friction stir welding.
This welding technology can also be used to sheets with different materials and a thickness of up to 35 mm can be joined together. Metal foams can also be joined in this way.
For the tool itself, it can be stated that the wear is rather low. Nevertheless, the pin should be replaced after a weld seam with a total length of 3 km in order to ensure consistent quality.
Other welding processes: